Dislocated Shoulder
January 30, 2023
Blood Flow Restriction and Muscle Growth
April 5, 2023Rotator cuff injuries
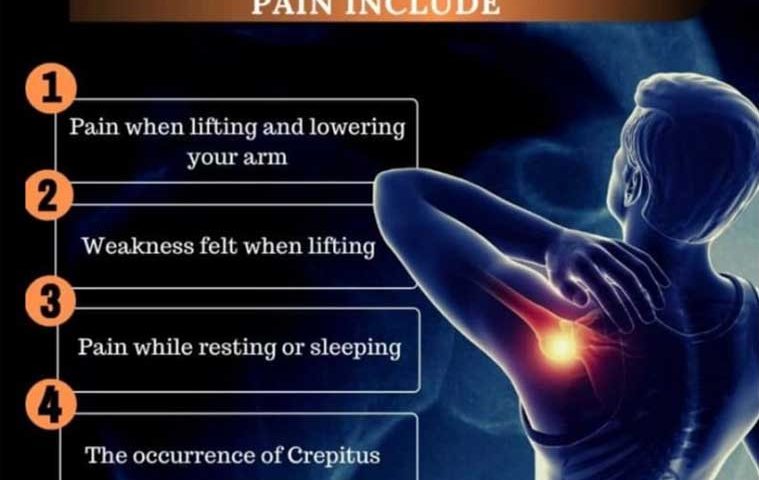
are most often caused by progressive wear and tear of the tendon tissue over time. Repetitive overhead activity or prolonged bouts of heavy lifting can irritate or damage the tendon. The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents.Signs of a rotator cuff tear include: Difficulty and pain caused by raising your arm. Popping or clicking sounds or sensations when moving your arm. Shoulder pain that worsens at night or when resting your arm.Rotator cuff injuries often result in a dull ache that can be felt deep in the shoulder.
It can occur due to specific movements, such as lifting or lowering the arm. Some people experience discomfort during rest as well. Sleeping is often disturbed by pain, especially when lying on the affected shoulder.Most rotator cuff tears cannot heal on their own unless the injury is minor.
Some need short-term anti-inflammatory medication along with physiotherapy, whereas most need surgical intervention.The minimum time for recovery from rotator cuff tendonitis or a small tear is generally two to four weeks, and stubborn cases can take several months. Early on, the aim is to reduce swelling and inflammation of the tendons and relieve compression in the subacromial space.Conservative treatments — such as rest, ice and physical therapy — sometimes are all that’s needed to recover from a rotator cuff injury. If your injury is severe, you might need surgery.