CANADA DAY
July 7, 2025
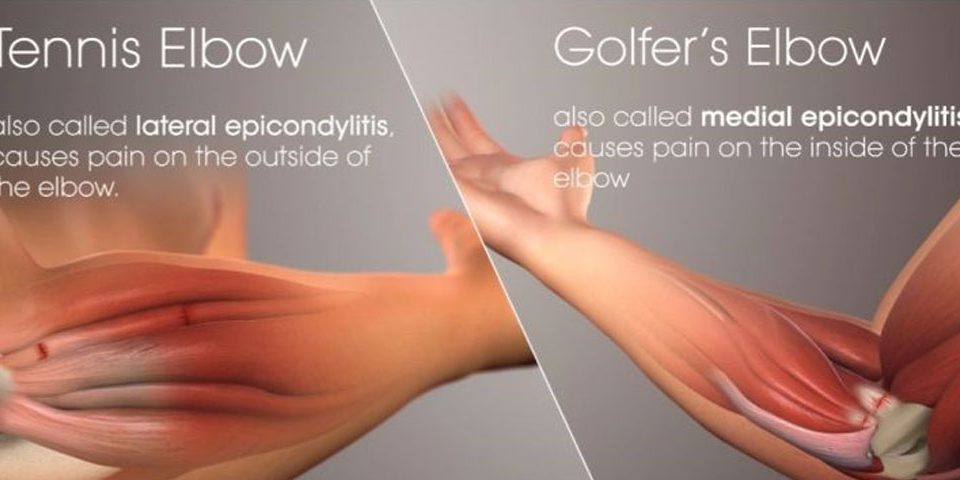
Tennis And Golfer Elbow
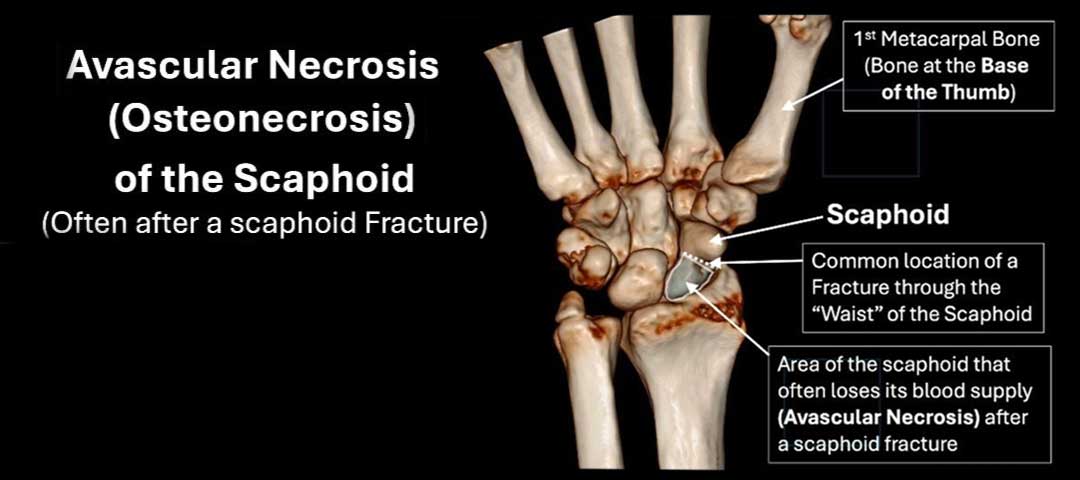
November 22, 2025Scaphoid Fracture
A scaphoid fracture is a break in the wrist’s scaphoid bone, a small boat-shaped bone located at the base of the thumb. It’s a common wrist fracture, accounting for 60–70% of carpal bone breaks. Scaphoid fractures are often caused by falling on an outstretched hand, but can also be caused by car accidents or contact sports. Scaphoid fracture symptoms often appear in the anatomic snuffbox, located at the base of the thumb. Pain and swelling are the most common symptoms, and can range from mild to severe. Pain may increase when grabbing or lifting objects. Other symptoms include:
1. Tenderness: Especially on the thumb side of the wristÂ
2. Bruising: Around the wrist
3. Wrist weakness: Difficulty gripping or twisting the wrist or thumb
There is a risk that fractures of the proximal scaphoid will completely disrupt the blood supply, causing part of the scaphoid to necrose, or die. This phenomenon, called “avascular necrosis,” can cause long-term problems in the wrist.
The three most commonly used clinical tests for evaluation of patients with suspected scaphoid fracture include:Â anatomical snuff box tenderness, scaphoid tubercle tenderness, and pain on axial compression of the thumb.
To heal a scaphoid fracture faster, prioritize proper immobilization in a cast or splint, maintain a nutritious diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, and elevate the hand to reduce swelling. For some fractures, surgical fixation with a screw may shorten healing time, while low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) can also accelerate bone repair. Consistent medical follow-up and adherence to your doctor’s instructions are essential for the best outcome.